GPX to GeoJSON - Free Online Data Converter
Looking for how to convert GPX data into GeoJSON format? Use this GIS data converter for free.
GPX data format is spatial data type mostly used in GPS devices to store your outdoor activity in the form of waypoints and tracks. Outdoor activity can be your fitness routine walking, running or hiking or may be some professional work like capturing coordinates of road signs, surveying fiber optic lines, pipelines, power electric infrastructure ets.
GPS devices are used by GIS professionals, and outdoor enthusiasts very commonly. Mostly GPS devices store the data in GPS exchange data format and GPX data format is one of them.
This absolutely free online web mapping tool helps you to convert you data retrieved from the GPS device to well known GIS data format geojson. Sample GPX Data to Download.
Geodata Converter Key Features:
User Guide: How to convert GPX to GeoJSON Step by Step Guide:
This guide will help you to use online GPX to GeoJSON free converter.
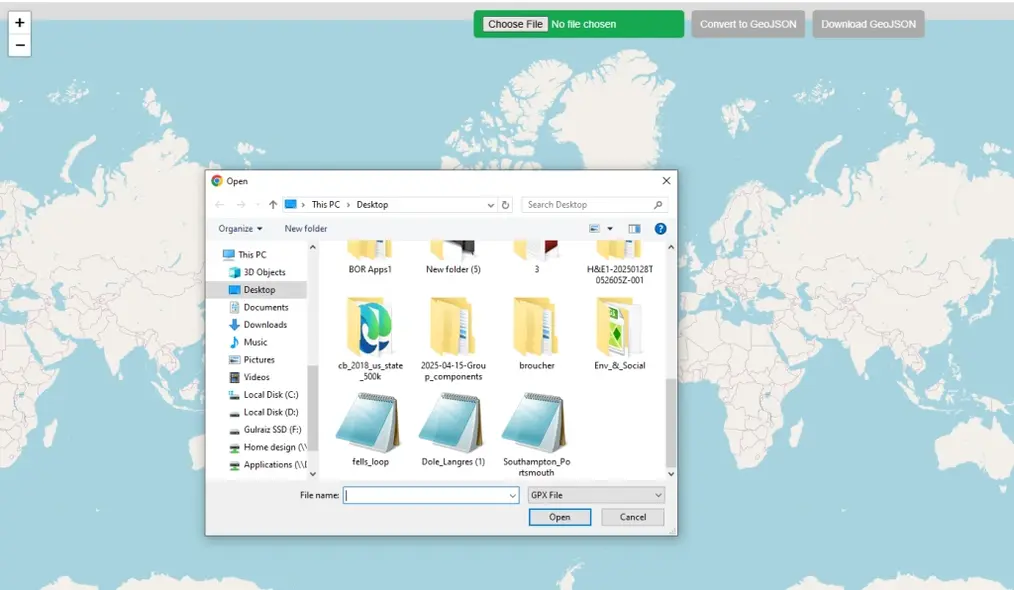
Step 1: Upload Data
Click on green button on top of map to choose file. File browser will be opened, locate the GPX file in your local PC directory and open. This free online web mapping tool will read the spatial data automatically and zoom map to the extent of the data.
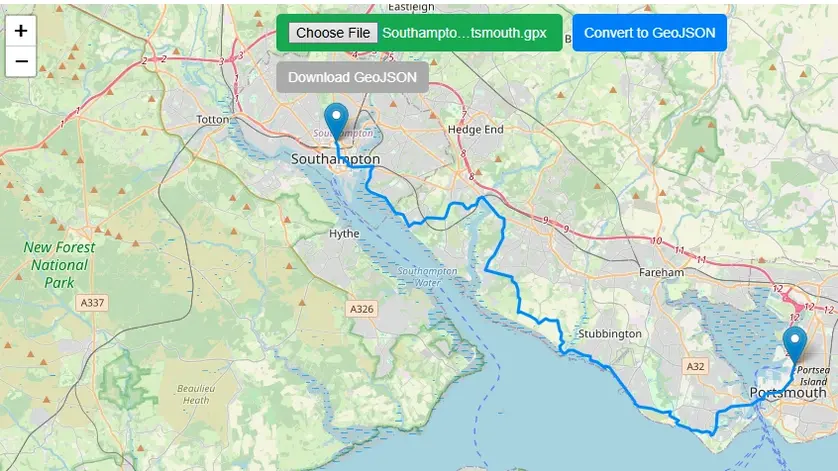
Step 2: Convert Data
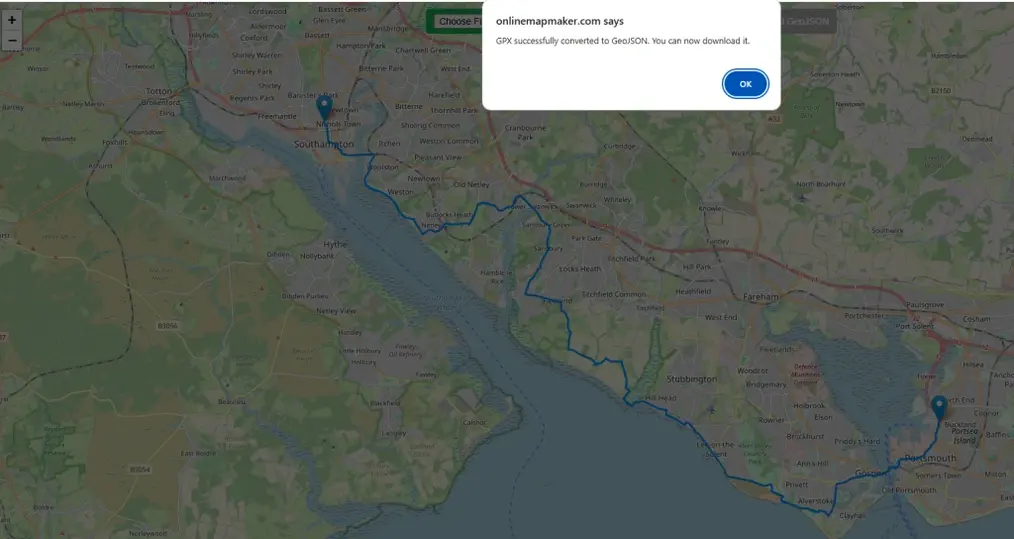
Once data is uploaded and displayed on map Convert to geoJSON button will be turned blue and active. Press the button and an alert will be popped up on top of the web browser, showing “GPX successfully converted to GeoJSON. You can now download it.”
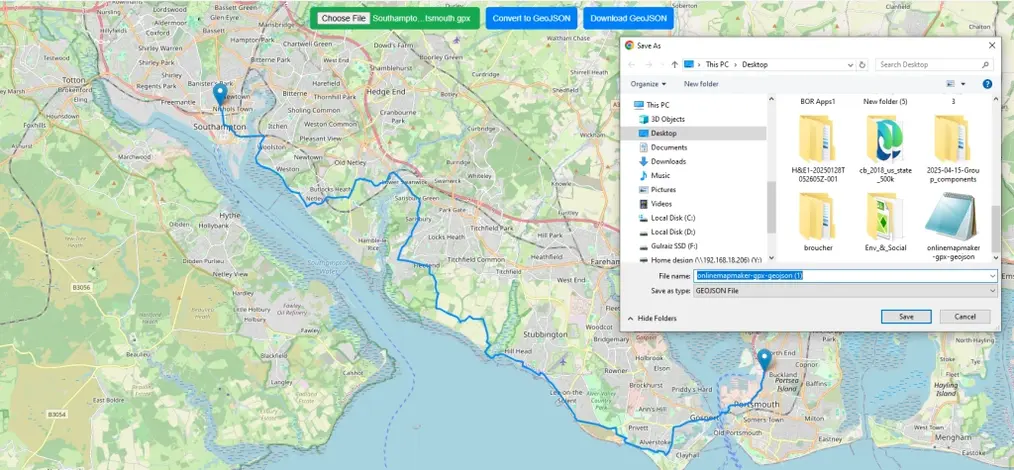
Step 3: Download geoJSON
After converting the data “Download GeoJson” will be turned blue and activated. Simply click the button to download and save it to your computer.
Now you can use and view this data in any GIS software like QGIS, ArcGIS etc.
A Brief History of the GPX File Format
Name: GPS eXchange Format (GPX)
Launch Date: The first version, GPX 1.0, was introduced in 2002.
Core Principle: It was an open standard, freely available for anyone to use without royalties or restrictions.
Foundation: It was built using XML (eXtensible Markup Language), which is human-readable and easy for software to parse. This was a key to its widespread adoption.
The Development of GeoJSON
The Developers: The MetaCarta Incubator
The initial drive for GeoJSON came from developers at MetaCarta, Inc., a company focused on geographic search and referencing technology (later acquired by Nokia and then Microsoft).
Primary Authors
- Chris Helm - Principal author and driving force behind the initial specification
- Martin Daly - Instrumental in the design and early advocacy of the format
The "Others"
The original specification drafting was a collaborative effort. While Helm and Daly were the leads, other developers within and connected to MetaCarta's ecosystem contributed to the discussions and early implementations.
The Original GeoJSON.org Specification (2008)
Archive Link: https://web.archive.org/web/20160715202627/http://geojson.org/geojson-spec.html
"This specification was developed by Chris Helm, Martin Daly, and others..."
The Big Idea: Leveraging the JSON Ecosystem
The choice of JSON was a deliberate and strategic decision based on several key advantages over the existing standard, Geography Markup Language (GML), which was based on XML.
| Characteristic | JSON's Advantage for Web Development |
|---|---|
| Lightweight | Less verbose than XML, resulting in smaller file sizes and faster transmission |
| Native Support | Could be directly parsed in any web browser using JSON.parse() |
| Data Structure | Mapped perfectly to fundamental programming concepts |
| Human-Readable | Easier for developers to read and debug |
Butler, H., et al. (2016). RFC 7946 - The GeoJSON Format
Link: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7946
The official IETF standard acknowledges this lineage and rationale.
The Goal: A Simple, Unified Feature Model
The goal was to create a practical format for the most common use cases of web mapping: displaying and interacting with geographic Features.
The core data model:
{
"type": "Feature",
"geometry": {
"type": "Point",
"coordinates": [-105.01621, 39.57422]
},
"properties": {
"name": "My Favorite Location",
"type": "Coffee Shop",
"rating": 5
}
}
This structure achieves:
- Simple Geographic Features: The
geometryobject handles points, lines, and polygons - Non-Spatial Properties: The
propertiesobject stores associated data - Easy to Parse: The entire structure is a standard JSON object
The GeoJSON Standard (IETF RFC 7946 - Section 1.3)
Link: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7946#section-1.3
"A Feature object has a 'type' member with the value 'Feature'... A Feature object has a member with the name 'geometry'... A Feature object has a member with the name 'properties'..."
Open Source Resources